eCAL in Docker
Here we will show how to deploy eCAL into a docker container, and how to use its image from other containers.
Prerequisite
-
Install Docker as described in the Docker installation documentation
-
Optional: If you want your docker container to talk to eCAL Nodes on other machines: Set up your multicast routes on the host.
-
Optional: If you want to use eCAL on your host to subscribe to data from your docker containers: Install eCAL the host.
Getting Started
In this tutorial we are going to create:
- A general purpose eCAL Docker container
- A publisher container with a custom Hello World Publisher
- A subscriber container receiving the Hello World data.
The file hierarchy that we are going to follow:
Directoryecal_in_docker
- docker-compose.yaml
Directoryecal_runtime_container
Directorypub_container
Directorysub_container
eCAL runtime container
-
Create the file
ecal_runtime_container/Dockerfileand paste the following installation commands:Dockerfile 1# Base image:2FROM ubuntu:focal34# Install eCAL from PPA:5RUN apt-get update && \6apt-get install -y software-properties-common && \7rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*8RUN add-apt-repository ppa:ecal/ecal-latest9RUN apt-get install -y ecal1011# Install dependencies for compiling the hello world examples.12# You can omit this, if you don't want to build applications in the container.13RUN apt-get install -y cmake g++ libprotobuf-dev protobuf-compiler1415# Set network_enabled = true in ecal.ini.16# You can omit this, if you only need local communication.17RUN awk -F"=" '/^network_enabled/{$2="= true"}1' /etc/ecal/ecal.ini > /etc/ecal/ecal.tmp && \18rm /etc/ecal/ecal.ini && \19mv /etc/ecal/ecal.tmp /etc/ecal/ecal.ini2021# Print the eCAL config22RUN ecal_config -
Build the image:
Terminal window cd ecal_in_dockersudo docker build . --rm -t ecal-runtime -
Test the image
Terminal window sudo docker run --rm -it --ipc=host --pid=host --network=host ecal-runtimeAt this point you are in the docker container. You can exit it with
exit. If you runecal_sample_person_sndin the docker container and have an eCAL installation on your host, you can subscribe to the data via the eCAL Monitor orecal_sample_person_rec.
Publisher container
The publisher container will be built on top of the ecal-runtime container.
It will contain the Hello World Sample from the Getting Started Section.
-
Create a file
pub_container/Dockerfileand paste the following content:Dockerfile 1#ecal base image:2FROM ecal-runtime34WORKDIR /src/pub56COPY CMakeLists.txt main.cpp ./7RUN cmake . && make8CMD ./hello_world_snd -
Create publisher source code:
pub_container/main.cppmain.cpp 1#include <ecal/ecal.h>2#include <ecal/msg/string/publisher.h>34#include <iostream>5#include <thread>67int main(int argc, char** argv)8{9// Initialize eCAL. The name of our Process will be "Hello World Publisher"10eCAL::Initialize(argc, argv, "Hello World Publisher");1112// Create a String Publisher that publishes on the topic "hello_world_topic"13eCAL::string::CPublisher<std::string> publisher("hello_world_topic");1415// Create a counter, so something changes in our message16int counter = 0;1718// Infinite loop (using eCAL::Ok() will enable us to gracefully shutdown the19// Process from another application)20while (eCAL::Ok())21{22// Create a message with a counter an publish it to the topic23std::string message = "Hello World " + std::to_string(++counter);24std::cout << "Sending message: " << message << std::endl;25publisher.Send(message);2627// Sleep 500 ms28std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(500));29}3031// finalize eCAL API32eCAL::Finalize();33} -
Create file
pub_container/CMakeLists.txtCMakeLists.txt 1cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0)2set(CMAKE_FIND_PACKAGE_PREFER_CONFIG ON)34project(hello_world_snd)56set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14)7set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD_REQUIRED ON)89find_package(eCAL REQUIRED)1011set(source_files12main.cpp13)1415add_executable(${PROJECT_NAME} ${source_files})1617target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME}18eCAL::core19) -
Build the image:
Terminal window cd pub_containersudo docker build . --rm -t ecal-publisher:1.0.0
Subscriber container
The subscriber container will also be based on the ecal-runtime container and contain the Hello World Sample from the Getting Started Section.
-
Create a file:
sub_container/DockerfileDockerfile 1#ecal base image:2FROM ecal-runtime34WORKDIR /src/sub56COPY CMakeLists.txt main.cpp ./7RUN cmake . && make8CMD ./hello_world_rec -
Create subscriber source code:
sub_container/main.cppmain.cpp 1#include <ecal/ecal.h>2#include <ecal/msg/string/subscriber.h>34#include <iostream>5#include <thread>67// Callback for receiving messages8void HelloWorldCallback(const std::string& message)9{10std::cout << "Received Message: " << message << std::endl;11}1213int main(int argc, char** argv)14{15// Initialize eCAL16eCAL::Initialize(argc, argv, "Hello World Subscriber");1718// Create a subscriber that listenes on the "hello_world_topic"19eCAL::string::CSubscriber<std::string> subscriber("hello_world_topic");2021// Set the Callback22subscriber.AddReceiveCallback(std::bind(&HelloWorldCallback, std::placeholders::_2));2324// Just don't exit25while (eCAL::Ok())26{27std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(500));28}2930// finalize eCAL API31eCAL::Finalize();32} -
Create file
sub_container/CMakeLists.txtCMakeLists.txt 1cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0)2set(CMAKE_FIND_PACKAGE_PREFER_CONFIG ON)34project(hello_world_rec)56set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14)7set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD_REQUIRED ON)89find_package(eCAL REQUIRED)1011set(source_files12main.cpp13)1415add_executable(${PROJECT_NAME} ${source_files})1617target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME}18eCAL::core19) -
Build the image:
Terminal window cd sub_containersudo docker build . --rm -t ecal-subscriber:1.0.0
Run the docker containers
-
You can run the publisher and subscriber images manually with
docker run.Terminal window sudo docker run --rm -it --ipc=host --network=host --pid=host ecal-subscriber:1.0.0sudo docker run --rm -it --ipc=host --network=host --pid=host ecal-publisher:1.0.0 -
You can also use the docker-compose file to manage multiple containers.
-
In the parent folder create file
docker-compose.yamland paste the following content:docker-compose.yaml 1version: "3"23services:4subscriber:5build: ./sub_container6image: ecal-subscriber:1.0.07container_name: ecal-subscriber8network_mode: host9ipc: host10pid: host11publisher:12build: ./pub_container13image: ecal-publisher:1.0.014container_name: ecal-publisher15network_mode: host16ipc: host17pid: host -
You can now use that docker-compose to build/run the publisher and subscriber containers:
Terminal window sudo docker-compose buildsudo docker-compose up
-
Seamless IPC-Communication across host borders
In eCAL, you are able to set host belonging over network borders by utilizing the ecal.ini configuration file with the same host_group_name - in the following steps, you will learn how to set this up.
-
To encapsulate your container network from your host network, you need to create a new docker network with the following command:
Terminal window sudo docker network create --driver=bridge --subnet=10.0.10.0/24 my_network -
Edit your
ecal.iniand run your Container within the newly created docker network-
You will use our previously discussed ecal-runtime-image for the next step.
-
First, open
/etc/ecal/ecal.inifrom your preferred editor. -
Search for the line
network_enabledand set it totrue. -
Search for the line
host_group_nameand write your preferred name. -
Save and close the
ecal.inifile. -
Now your
ecal.inifile is prepared. We want to use it not only for our Host-System but also for our Container, so we don’t need to edit theecal.iniin our Container again. To achieve that, run following command to start your container:
Terminal window sudo docker run --rm -it --ipc=host --pid=host --network=my_network --name=container1 -h=container1 --ip=10.0.10.10 -v /etc/ecal/ecal.ini:/etc/ecal/ecal.ini ecal-runtime-
You should now be inside the root shell of your Container. Check if your
ecal.inifile is correct. -
Now your Container is prepared and configured correctly, so we are ready to start an eCAL example.
Terminal window ecal_sample_person_snd -
-
Configure the Host network
- eCAL is sending UDP messages to a multicast IP group
239.0.0.0/24, further information in Getting Started Section. The idea is now, to successfully receive those messages from your previously started container on your host. For that, you need to add a route to your routing table. By typingifconfigin your shell, you can identify the right docker network. In our case, the prefix of the docker network is alwaysbrfollowed by random numbers. After identifying the right network, run following command.
Terminal window sudo ip route add 239.0.0.0/24 dev <br-xxx> metric 1- Review your network configuration. Your eCAL-Monitor should resemble this example:
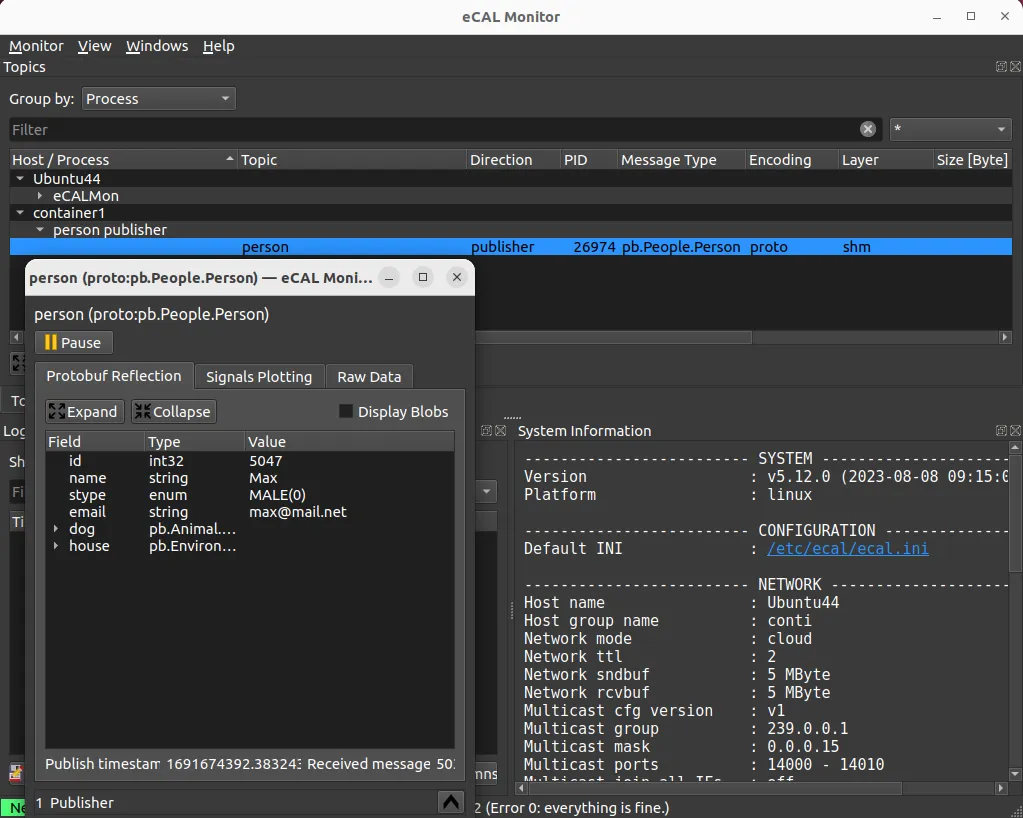
- eCAL is sending UDP messages to a multicast IP group
-
(optional) After adding the route, you register the Container with IP address and name in /etc/hosts for DNS resolution, enabling easy access to it by hostname within the network.
Terminal window sudo nano /etc/hosts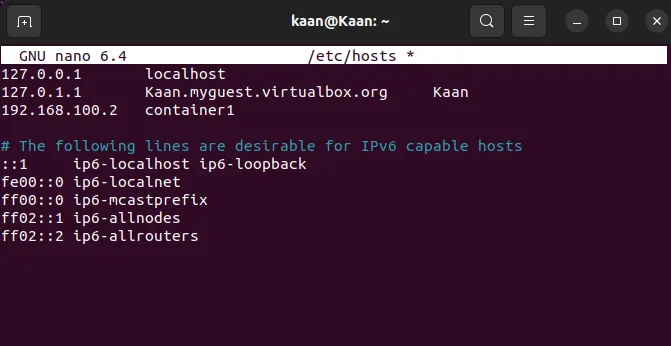
When you are done, all eCAL nodes can communicate seamlessly from docker to the host and vice versa.